Contact Us
- Home
- Contact us
Best Heart Failure Surgeon in South Mumbai
best doctor a muscular valve, the heart pumps blood to different parts of the body. Heart failure happens when the heart's pump weakens and is unable to circulate enough blood to meet the body's needs.
Heart Failure Signs And Indicators Could Include:
Breathing difficulties during exercising or sleeping
Weakness and exhaustion; swelling in the legs, ankles, and feet;
An erratic or rapid pulse; a decrease in exercise ability.
Persistent coughing or wheezing with bloody mucous that is either pink or white
Abdominal swelling -significant weight gain as a result of fluid retention
A decrease in hunger and nauseous
Difficulty focusing or becoming less vigilant
Chest pain may be experienced if a heart attack is the cause of heart failure.
Heart Failure Causes And Risk Factors:
Heart disease
Heart valve dysfunction
Elevated blood pressure.
Abnormal heartbeats
Congenital cardiac illness
Congenital disorders in the heart
Diabetes Drinking alcohol
Using or smoking tobacco
Being overweight
Hereditary cardiac disorders
Reactions brought caused by allergens
Any illness that has a systemic impact
Hematomas in the lungs
Severe infections
Using specific drugs
Types Of Heart Failure:
Breathlessness is a consequence of fluid accumulation in the lungs due to left-sided heart failure.
Right-sided heart failure: Fluid backup into the legs, foot, and belly may cause swelling.
Systolic heart failure: characterized by an inefficient pump and improper cardiac contractions in between beats.
Diastolic heart failure: also referred to as "heart failure with preserved ejection fraction," is a disorder in which the heart's left ventricle, the lower left chamber, is unable to fill with blood adequately during the diastolic phase, reducing the volume of blood that is pumped out to the body
Heart Failure Prevention:
Lowering your risk factors is the key to preventing heart failure. Adopting a healthy lifestyle and taking the prescribed medications by our doctor will help decrease or eliminate many of the risk factors associated with heart disease.
You can alter your lifestyle to help prevent heart failure by doing the following:
Refrain from smoking.
Managing a few illnesses, such diabetes and hypertension
Continuing to exercise
Eating a diet rich in nutrients
Maintaining a healthy weight
Controlling and lowering your stress level
What Symptoms Indicate Heart Failure?
A number of tests can be performed to confirm the diagnosis of heart failure once there is a suspicion of it.
ECG: It can reveal information about previous heart attacks, which may be the cause of heart failure. Furthermore, if medical therapy is unsuccessful, the ECG will help us determine whether this patient qualifies for cardiac resynchronization therapy.
2D Echo & Doppler: This type of ultrasound of the heart allows us to measure the dimensions of its various chambers, check for heart valve leaks, and evaluate the left ventricle's ejection fraction (LVEF) to determine how well the heart is working. A normal person's LVEF is greater than 60%; if it is lower, that person is more likely to develop heart failure.
NTproBNP: Individuals with heart failure have elevated levels of this blood marker. This is helpful in situations where the etiology of dyspnea is unclear, as lung conditions are typically the culprit. Physicians can diagnose heart failure in a patient when nTproBNP levels are elevated.
What Is The Optimal Course Of Action For Heart Failure?
Searching for any reversible causes of heart failure is the first step. If the root cause of heart failure is treated, the condition will get better on its own. For instance, the heart gets less blood if cardiac artery obstructions are the cause of heart failure, which weakens the heart muscle. By using coronary angioplasty or CABG surgery to unblock blockages, we can treat heart failure and enhance heart function.
It is common practice to recommend dietary and lifestyle changes when treating heart failure. Among the suggestions are:
Treatment For Heart Failure:
Medication: A combination of drugs is usually used to treat heart failure. To address underlying disorders, you might need to take one or more drugs.
Coronary artery bypass: surgery may be recommended by your doctor if your heart failure is brought on by significantly clogged arteries. Your heart's clogged arteries are joined below and above by a healthy blood vessel taken from your leg, arm, or chest. The cardiac muscle receives more blood via the new channel.
Repair or replacement of a heart valve: Your doctor may suggest either action if your heart failure is being brought on by a malfunctioning heart valve. By replacing the valve flaps or excising extra valve tissue, surgeons can fix the valve and enable the leaflets to seal tightly. The ring that covers the valve may need to be replaced or tightened in order to repair the valve.
Heart valve replacement or repair: can be done as minimally invasive surgery, open heart surgery, or as a cardiac procedure that uses catheters—flexible tubes—for the heart (cardiac catheterization).
Cardiac Resynchronization Therapy (CRT): This treatment helps the heart circulate blood evenly and efficiently across the chambers.
Mechanical Circulatory Support (MCS): To maintain blood flow and pumping through the body's tissues, a heart-connected device called a ventricular assist device (VAD) can be implanted in the abdomen. Patients who are waiting for a heart transplant or who have end-stage heart failure but are not transplant candidates may benefit most from it in terms of increased survival and quality of life.
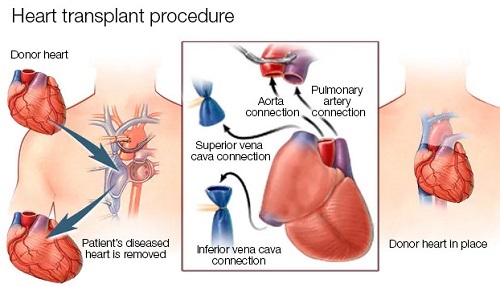
A heart transplant is carried out: For certain individuals, medicine or surgery are not effective due to their extreme heart failure. These individuals might require cardiac transplantation with a viable donor heart.
The Most Common Recommendation Is To Consume Less Water And Salt.
Increased fluid retention in the lungs and other bodily regions can be brought on by a diet high in salt. Restricting salt intake can therefore help to manage the symptoms of heart failure. The conventional wisdom is to stay away from pickles, namkeens, and table salt. It's also very important to drink enough water.
It is advised that those with severe heart failure consume no more than 1.5 liters of fluid per day. The term "fluids" includes soups, milk, tea, curd, and water. To monitor your fluid levels, weigh yourself at the same time each day on the same scale. One sign that you're holding on to more fluid than you should is weight gain.
Manage your weight: If you are overweight, your heart needs to work harder to pump blood and oxygen to your body. Losing weight can help you feel better and alleviate stress on your heart.
Limit your alcohol intake because it can harm your heart, particularly if you already have heart failure.
Medication: A number of drugs are available to help enhance cardiac function; these drugs should be taken in addition to a change in lifestyle.
Cardiac Resynchronization treatment - If drugs do not work than certain patients with heart failure may benefit from (CRT-P/CRT-D (Cardiac Resynchronization therapy) device. Similar to a pacemaker, this device resynchronizes heart contractions by inserting three wires inside the heart, improving cardiac function.
Heart Transplantation: Patients who do not respond to treatment may require heart transplant surgery or an artificial heart (also known as a left ventricular assist device, or LVAD).
Why Select Your Heart Failure Surgeon from Dr. Amit Karad Shad?
After thoroughly knowing his patient's condition and medical history, Dr. Amit Karad performs heart transplant surgery. We usually require several days to assess a patient with heart failure. In order to identify possibly treatable causes of heart failure, we also conduct a thorough biochemical examination. We review medical records, therapies received, and other medical/surgical issues that may preclude transplantation (e.g., advanced age, cancer, active infections, serious kidney or liver failure, alcohol addict reluctant to stop drinking). When it is determined that a patient will only benefit from a heart transplant, the patient is added to the active transplant waiting list in order to receive a donor organ claim. Dr. Amit Karad a south Mumbai-based physician

