Contact Us
- Home
- Contact us
Best Valve Replacement and Repair Surgeon in South Mumbai
For people with heart valve conditions—conditions where the heart's valves malfunction and cause a variety of cardiac problems—heart valve surgery may be a life-saving procedure that requires heart valve replacement or repair. Saifee Hospital's staff of exceptionally talented cardiac surgeons specializes in both kinds of heart valve operations. We are a reliable option for anyone looking for the greatest care available and heart valve repair or replacement due to our dedication to cutting edge medical procedures, patient-centered care, and medical developments.
What is Heart Valve Surgery?
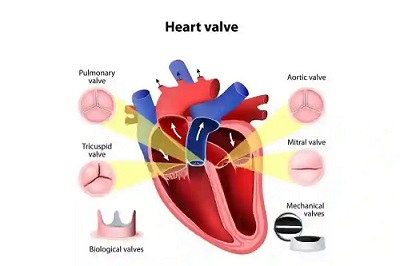
One approach for treating heart valve dysfunction is heart valve surgery. This occurs when there is a malfunction in one of the four cardiac halves that is in charge of pumping blood in the appropriate direction. Our heart is essentially a pump made of muscle tissue. It has four chambers that are in charge of pumping. The lower chambers are referred to as ventricles, and the upper chambers as atria. There are valves in between each of these chambers that make sure blood flows through the heart in the proper directions.
Pulmonary valve: Is located between the pulmonary artery and the right ventricle.
Tricuspid valve: Between the right atrium and the right ventricle is the tricuspid valve.
Mitral valve: This one is situated in the space between the left atrium and the left ventricle.
Aortic valve: This one is situated between the left ventricle and the aorta.
Every valve is made up of flaps called cusps for aortic and pulmonary valves and leaflets for tricuspid and mitral valves. Every heartbeat causes these valves to open and close. Sometimes the valves can't close and open as they should, which impacts how well blood flows from the heart to the body. Medical intervention is necessary if any of the valves are diseased or damaged. Therefore, a heart valve surgery involves the surgeon replacing or repairing the damaged heart valves. Actually, the two valves that are changed the most frequently are the aortic and mitral valves. Replacement of the tricuspid and pulmonary valves occurs occasionally. This encompasses a variety of cardiac surgery techniques, such as open and minimally invasive heart surgery.
Conditions That May Require A Heart Valve Surgery
Heart valve disease frequently develops either before birth or during a person's lifetime. Furthermore, the causes are still unknown in a lot of situations. The following are common causes of heart valve problems:
Congenital valve disease affects the aortic or pulmonic valve. These include missized valves or improperly shaped leaflets. The leaflets are frequently not correctly connected.
Aortic valve is impacted by bicuspid aortic valve disease. This valve only has two cusps, or leaflets, as opposed to a typical valve's three. The third leaflet is missing, which makes the valve stiff and makes it difficult for it to close and open properly. In close proximity, it can also turn green and cause resistance.
Acquired Valve Disease: Individuals with this condition have issues that have developed over time. It involves modifications to the valve structure brought on by an infection or illness, such as endocarditis or rheumatic fever.
Endocarditis: When bacteria enter the bloodstream and begin attacking the valves, this condition is brought on. Consequently, the valve starts to develop holes and growths, which also cause scarring. Leaky valves result from this. The bacteria that cause endocarditis can enter the bloodstream through IV medication use, serious illnesses, dental work, and surgery.
Symptoms For Heart Valve Disease
These are a few of the most typical signs that a heart valve needs to be replaced or repaired.
Breathlessness: This is most obvious when you lie down on the bed or are deeply engaged in everyday tasks. To make breathing easier, you must always have a couple cushions beneath your head.
Weakness or Dizziness: You constantly feel short on energy and experience dizziness while performing daily tasks. There may also be situations in which you unexpectedly pass out.
Chest Discomfort: You can experience some pressure or discomfort in your chest. When you're outside in the cold or in a windy atmosphere, it can get worse.
Constant Palpitations: If you experience palpitations on a regular basis, which include an elevated heart rate, an erratic heartbeat, a flip in the chest, or skipped beats, this is cause for concern.
Swollen feet, ankles, or abdomen: Pulmonary edema is the term used to describe this illness. It is possible for your tummy to enlarge, making you feel bloated.
Unexpected Weight Gain: A rapid rise in weight that occurs without any apparent food changes or excesses.
Diagnosis before Heart Valve Surgery
Before proposing a heart valve repair or replacement procedure, your heart valve repair best doctor will do a comprehensive examination, have a long talk with you, and order specific tests.
During the physical examination, you will hear your heart's valves opening and closing. The swishing sound that the blood makes as it flows past a stenotic or leaky valve is known as a cardiac murmur. In a similar vein, an enlarged heart is indicated by an erratic rhythm. In fact, best doctor can listen to your lungs to determine whether your heart is pumping poorly due to fluid retention. A comprehensive physical examination that evaluates the body's circulation and other organs' functionality comes next.
Transoesophageal Echocardiography (TEE) is a specialist cardiac imaging technique that is particularly useful for evaluating heart valve issues. It involves inserting a probe into the oesophagus to get clear images of the structure and function of the heart.
Echocardiography also called a "echo," is a popular non-invasive imaging technique that employs sound waves to produce real-time images of the heart in order to monitor and diagnose a number of cardiac disorders, including issues with the heart valves.
Cardiac Catheterization (Angiogram): Often called a "angiogram," this procedure entails inserting a contrast dye into the heart's blood vessels via a thin, flexible tube (catheter). This enables medical professionals to see irregularities in the coronary arteries and make diagnoses. The results of these tests are used to diagnose the progression of the valve disease and to prescribe a different course of treatment.
Heart Valve Repair
When feasible, the physician recommends heart valve repair because it preserves the valve and ensures that the heart functions properly. It consists of:
The sick valve's hole was closed by the surgeon.
Reconnecting the valve cusps comes next
To enable the valves to seal firmly, any extra oil between them should be removed.
Repairing the valves with new cables to provide structural support
Disconnecting the fused valves
Tightening of the annulus, or ring, surrounding the valve
Replacement of Heart Valve
Best doctors advise heart valve replacement when heart valve repair is completely unfeasible. The heart valve must be removed and replaced with either a mechanical valve or one made of human, pig, or cow heart tissue.
Additionally, because these living tissue valves deteriorate with time, replacement is inevitable. However, if you have a mechanical valve, you will need to take blood thinners for the rest of your life to prevent blood clots.
Before choosing a course of action, the patient is informed about the advantages and disadvantages of each type of valve replacement. Using a catheter procedure, this operation involves a minimum invasion
Getting Ready for Heart Valve Surgery
Making the necessary preparations for heart valve surgery is essential to a successful procedure and a quicker recovery. While getting ready for heart valve surgery, keep the following crucial things in mind:
Consultation and Education: Arrange a meeting with your cardiac surgeon to go over the objectives of the procedure, as well as the advantages and disadvantages. Make inquiries and look for clarification on what to anticipate.
Medical examination: All patients must have a thorough medical examination, which may involve imaging studies, blood testing, and other diagnostic procedures.
Cardiac Rehabilitation: To enhance their general health and physical fitness, patients may occasionally be mandated to engage in a cardiac rehabilitation program prior to surgery.
Medication: In the days preceding surgery, cardiac experts may occasionally ask patients to modify or stop taking specific drugs, like blood thinners.
Diet and Nutrition: In order to support their body's nutritional requirements and general well-being, patients must adhere to any food restrictions or fasting guidelines that may be given.
Stop Smoking: If you smoke, you should think about giving it up before surgery. Smoking might hinder the healing process and raise the risk of complications.
Mental and Emotional Preparation: To help reduce anxiety, patients can turn to friends, relatives, or a counselor for emotional support. They can also think about joining a support group.
Heart Valve Surgery Risks
The patient's age, general health, the type of valve surgery required, and the surgical team's experience all affect the overall risk profile for heart valve surgery. The Saifee Hospital team of cardiologists and cardiac surgeons carefully evaluates these risks and goes over them with patients prior to operation. The following are a few dangers connected to heart valve surgery:
Bleeding: One of the most prevalent risks following surgery is bleeding. Although surgeons take steps to minimize bleeding, severe bleeding may require further procedures or blood transfusions to treat. Infection: Surgical sites can get infected. To cure this infection, doctors may prescribe antibiotics or, in extreme situations, perform more surgery.
Blood Clots: Following surgery, blood clots may form in the heart or blood arteries. These clots have the potential to spread to other bodily parts and result in consequences like strokes.
Stroke: Dislodging blood clots or plaque during surgery increases the chance that they will travel to the brain and cause a stroke. Surgeons take action to lower this danger.
Stroke: Dislodging blood clots or plaque during surgery increases the chance that they will travel to the brain and cause a stroke. Surgeons take action to lower this danger.
Heart Rhythm Issues: Surgery may cause an electrical disturbance in the heart, which can result in arrhythmias, or irregular heartbeats. Although they are typically transient, therapy may be necessary. Aesthesia and blood flow variations during surgery can put the kidneys under stress, which increases the risk of acute kidney damage (AKI). Usually transient, this gets better with the right attention.
Pneumonia and Respiratory Complications: Due to decreased lung function or postoperative immobilization, individuals following surgery are susceptible to pneumonia or other respiratory complications.
Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT): Blood clots in the legs' deep veins are caused by this condition, which is made more likely by immobility following surgery. In the event that these clots break free and move to the lungs, they may be hazardous (pulmonary embolism).
Heart Attack: Due to variations in blood flow and other reasons, heart attacks are uncommon but can happen during or after heart valve surgery.
Complications with Prosthetic Valve: Patients who receive biological (tissue) or mechanical heart valves run the risk of experiencing problems with the valves, such as blood clots accumulating on the mechanical valves or the need for additional valve surgery.

